Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
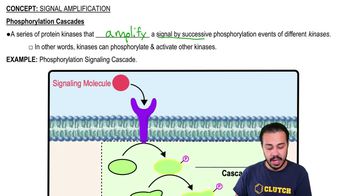
Phosphorylation Cascade
A phosphorylation cascade is a series of biochemical events where one enzyme phosphorylates another, leading to a chain reaction that amplifies a signal within a cell. This process is crucial in cellular signaling pathways, allowing a small initial signal to produce a large response, often involving multiple kinases that sequentially activate each other.
Recommended video:
Kinases
Kinases are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy molecules, like ATP, to specific substrates, typically proteins. This phosphorylation can alter the activity, localization, or function of the target proteins, playing a vital role in regulating various cellular processes, including metabolism, cell division, and signal transduction.
Recommended video:
Signal Amplification
Signal amplification refers to the process by which a small initial signal is greatly increased through a series of biochemical reactions, often involving kinases and other signaling molecules. In the context of the phosphorylation cascade, each activated kinase can trigger the activation of multiple downstream proteins, resulting in a significant enhancement of the cellular response to the original signal.
Recommended video: