Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion, which is the movement of substances from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. In the context of osmosis, this process specifically involves the diffusion of a solvent, typically water, across a semipermeable membrane. This membrane selectively allows certain substances to pass while blocking others. The concept of osmotic pressure is crucial here; it refers to the pressure needed to prevent the flow of the solvent, indicating the strength of osmosis. A higher osmotic pressure signifies a stronger osmotic effect.
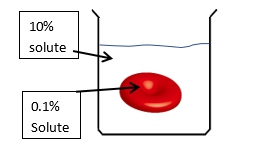
The direction of osmosis is influenced by the tonicity of the solutions involved, which refers to the relative concentrations of solutes in the solutions. There are three key terms used to describe tonicity: isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic. An isotonic solution has the same solute concentration as another solution, meaning there is no net movement of water. A hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration compared to another solution, leading to water moving into the cell, which can cause it to swell. Conversely, a hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration, resulting in water moving out of the cell, which can cause it to shrink.
These terms are comparative, meaning they are only meaningful when discussing two solutions in relation to each other. For example, when comparing the outside solution of a cell to the inside solution, if the outside solution has fewer solutes, it is hypotonic relative to the inside. If both solutions have equal solute concentrations, they are isotonic. If the outside solution has more solutes, it is hypertonic. Understanding these concepts is essential for predicting the direction of water movement during osmosis, which will be explored further in subsequent discussions.