Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Smooth Muscle Physiology
Smooth muscle is a type of involuntary muscle found in various organs, including the intestines and blood vessels. It is characterized by its non-striated appearance and ability to contract slowly and sustain contractions for extended periods. This unique physiology allows smooth muscle to perform essential functions such as regulating blood flow and facilitating digestion.
Recommended video:
Energy Efficiency in Muscle Contraction
Smooth muscle is known for its low energy consumption compared to skeletal muscle. It utilizes a mechanism called latch-bridge cycling, which allows it to maintain contraction with minimal ATP expenditure. This energy efficiency is crucial for functions that require prolonged contraction, such as maintaining vascular tone and peristalsis in the digestive tract.
Recommended video:
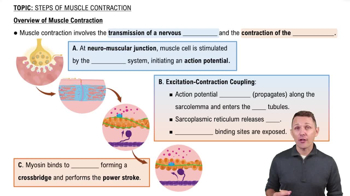
Overview of Muscle Contraction
Functional Role of Smooth Muscle
The primary function of smooth muscle is to control involuntary movements within the body. It plays a vital role in processes such as regulating blood pressure, moving food through the digestive system, and controlling airflow in the respiratory tract. Its ability to sustain contractions over time enables these systems to function effectively without constant energy input.
Recommended video: