Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acetylcholine (ACh) Receptors
Acetylcholine receptors are proteins located on the surface of muscle cells that bind to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. When ACh binds to these receptors, it triggers muscle contraction. Blocking these receptors prevents muscle contraction, making it a key mechanism for muscle relaxants used during surgery.
Recommended video:
Calcium Ion (Ca²⁺) Role in Muscle Contraction
Calcium ions play a crucial role in muscle contraction by facilitating the interaction between actin and myosin filaments within muscle fibers. When Ca²⁺ floods the cytoplasm, it initiates contraction. Therefore, a chemical that increases Ca²⁺ levels would promote muscle contraction rather than relaxation.
Recommended video:
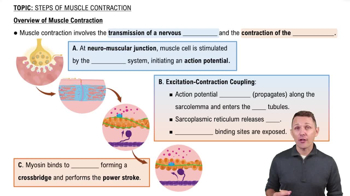
Overview of Muscle Contraction
Mechanism of Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants work by interfering with the neuromuscular transmission or the excitation-contraction coupling process. Effective skeletal muscle relaxants typically block ACh receptors or inhibit the release of ACh, leading to reduced muscle tone and paralysis, which is essential during surgical procedures to prevent involuntary movements.
Recommended video:
Introduction to Muscles and Muscle Tissue Example 1