Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Muscle Contraction Types
Muscle contractions can be categorized into two main types: isotonic and isometric. A slight contraction, often isotonic, involves a smooth and controlled shortening of the muscle, allowing for fine motor control. In contrast, a vigorous contraction is more forceful and can involve both isotonic and isometric components, leading to greater tension and power output.
Recommended video:
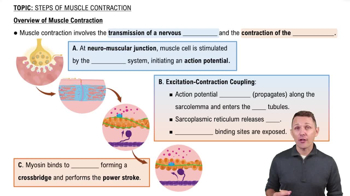
Overview of Muscle Contraction
Multiple Motor Unit Summation
Multiple motor unit summation refers to the process by which the nervous system recruits additional motor units to increase muscle force. During a slight contraction, fewer motor units are activated, resulting in a lower force output. Conversely, during a vigorous contraction, a larger number of motor units are recruited, leading to a significant increase in muscle tension and strength.
Recommended video:
Motor Unit Recruitment
Motor unit recruitment is the mechanism by which the body controls the strength of muscle contractions. Smaller motor units, which consist of fewer muscle fibers, are recruited first for light tasks, while larger motor units are activated for more intense efforts. This recruitment pattern allows for smooth transitions in force production, distinguishing between slight and vigorous contractions.
Recommended video:
Atoms- Smallest Unit of Matter
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance