Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a complex network of proteins and carbohydrates that provides structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. It plays a crucial role in tissue and organ structure, influencing cell behavior, migration, and differentiation. Understanding the composition and function of the ECM is essential for grasping how it maintains its position and interacts with cells.
Recommended video:
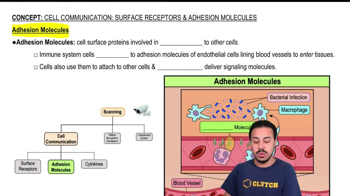
Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are proteins located on the cell surface that facilitate cell-to-cell and cell-to-ECM interactions. They are vital for the positioning of the ECM, as they help anchor the matrix to cells and guide its organization. The dynamics of CAMs are crucial for understanding how the ECM achieves its characteristic positioning within tissues.
Recommended video:
Matrix Remodeling
Matrix remodeling refers to the process by which the extracellular matrix is continuously broken down and rebuilt, allowing for adaptation to physiological changes. This process is mediated by enzymes such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and is essential for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the ECM. Understanding matrix remodeling is key to comprehending how the matrix reaches and maintains its characteristic position in response to various stimuli.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance