Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Photon Energy
The energy of a photon is determined by its wavelength, given by the equation E = hc/λ, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, c is the speed of light, and λ is the wavelength. For a CO2 laser emitting at 10.6 micrometers (um), this relationship allows us to calculate the energy of each photon, which is essential for determining how many photons are emitted per second based on the laser's power output.
Recommended video:
Intro to Energy & Types of Energy
Power and Energy Relationship
Power is defined as the rate at which energy is transferred or converted, expressed in watts (W), where 1 W = 1 J/s. In the context of the CO2 laser, the power output of 0.100 kW (or 100 W) indicates how much energy is delivered to the tissue per second. This relationship is crucial for calculating the total number of photons emitted per second by dividing the total power by the energy of a single photon.
Recommended video:
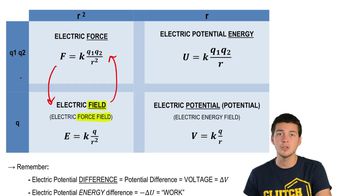
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Photon Flux
Photon flux refers to the number of photons passing through a given area per unit time, typically expressed in photons per second. To find the photon flux of the CO2 laser, one must divide the total power output of the laser by the energy of a single photon. This concept is vital for understanding the intensity of the laser's effect on tissue during surgical procedures.
Recommended video: