Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Photon Energy
The energy of a photon is determined by its wavelength and can be calculated using the formula E = hc/λ, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J·s), c is the speed of light (3.00 x 10^8 m/s), and λ is the wavelength. For a CO2 laser with a wavelength of 10.6 mm, this relationship is crucial for determining how much energy each emitted photon carries.
Recommended video:
Intro to Energy & Types of Energy
Power and Energy Relationship
Power is defined as the rate at which energy is emitted or transferred, measured in watts (W). In this case, the CO2 laser emits 7.50 mW, which is equivalent to 7.50 x 10^-3 W. To find the number of photons emitted per second, one must relate the total power output to the energy of individual photons, using the formula: Number of photons = Power / Energy per photon.
Recommended video:
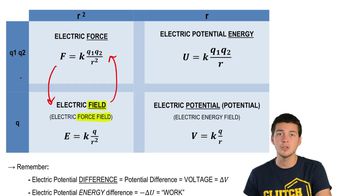
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Calculating Photons Emitted
To find the number of photons emitted per second by the laser, first calculate the energy of a single photon using its wavelength. Then, divide the total power output of the laser by the energy of one photon. This calculation provides the number of photons emitted per second, which is essential for understanding the laser's performance and applications.
Recommended video:
Calculating Dot Product Using Vector Components
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance