Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Index of Refraction
The index of refraction is a dimensionless number that describes how light propagates through a medium. It is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. A higher index indicates that light travels slower in that medium, affecting how light bends when entering or exiting different materials.
Recommended video:
Total Internal Reflection
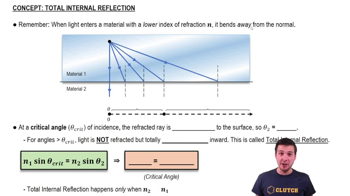
Total internal reflection occurs when a light wave traveling in a medium hits a boundary with a less dense medium at an angle greater than the critical angle. Instead of refracting, the light is completely reflected back into the denser medium. This phenomenon is crucial for applications like fiber optics and is dependent on the indices of refraction of the two media involved.
Recommended video:
Total Internal Reflection
Critical Angle
The critical angle is the minimum angle of incidence at which total internal reflection occurs. It can be calculated using the formula sin(θc) = n2/n1, where θc is the critical angle, n1 is the index of refraction of the denser medium, and n2 is that of the less dense medium. Understanding the critical angle is essential for determining the conditions under which light will reflect rather than refract at a boundary.
Recommended video: