Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering is the scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the light. This phenomenon explains why shorter wavelengths (blue and violet light) scatter more than longer wavelengths (red light), leading to the blue color of the sky. In the context of the question, it helps understand why the intensity of scattered light varies across different colors in the spectrum.
Recommended video:
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye, typically ranging from about 380 nm (violet) to 750 nm (red). Each color within this spectrum corresponds to a specific wavelength, with red light having the longest wavelength. Understanding the visible spectrum is crucial for analyzing how different colors of light are scattered and perceived.
Recommended video:
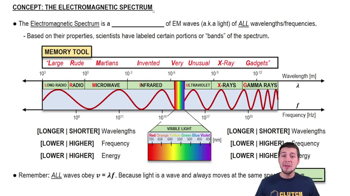
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Intensity of Light
The intensity of light refers to the power per unit area carried by a wave, which is perceived as brightness. In scattering phenomena, the intensity of scattered light can vary based on the wavelength of the incident light and the scattering mechanism involved. In this question, the intensity of scattered light in the red part of the spectrum can be derived from the intensity in the green part by applying the principles of scattering.
Recommended video: