Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law describes the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of an ideal gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature. This law is fundamental for understanding the behavior of gases under various conditions and is essential for calculating properties like heat capacities.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law
Molar Heat Capacity
Molar heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of a substance by one degree Celsius at constant volume (C_v) or constant pressure (C_p). C_v is typically lower than C_p because at constant pressure, work is done by the system as it expands. Understanding these concepts is crucial for thermodynamic calculations involving gases.
Recommended video:
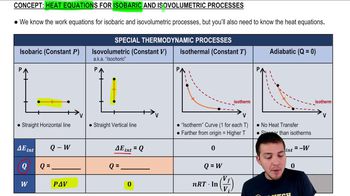
Heat Equations for Isobaric & Isovolumetric Processes
Specific Heat Ratio (γ)
The specific heat ratio, denoted as γ (gamma), is the ratio of molar heat capacities at constant pressure and volume (C_p/C_v). For ideal gases, this ratio is a key parameter that influences the behavior of the gas during processes such as adiabatic expansion or compression. Knowing γ helps in deriving relationships between heat capacities and is vital for solving problems related to thermodynamics.
Recommended video:
Specific Heat & Temperature Changes