Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
First Law of Thermodynamics
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. In the context of heat transfer into a system, the law can be expressed as ΔU = Q - W, where ΔU is the change in internal energy, Q is the heat added to the system, and W is the work done by the system. This principle is essential for understanding how heat energy is converted into work during the expansion of the gas.
Recommended video:
The First Law of Thermodynamics
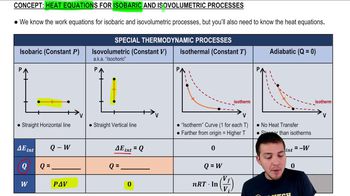
Isobaric Process
An isobaric process is a thermodynamic process that occurs at constant pressure. In this scenario, as heat is added to the monatomic ideal gas, it expands while maintaining constant pressure. The work done by the gas during this expansion can be calculated using the formula W = PΔV, where P is the pressure and ΔV is the change in volume, highlighting the relationship between heat, work, and volume change.
Recommended video:
Heat Equations for Isobaric & Isovolumetric Processes
Monatomic Ideal Gas
A monatomic ideal gas consists of single atoms and follows the ideal gas law, which relates pressure, volume, and temperature (PV = nRT). For monatomic gases, the specific heat capacities are well-defined, with the molar specific heat at constant pressure (C_p) being higher than that at constant volume (C_v). Understanding the properties of monatomic ideal gases is crucial for calculating the fraction of heat energy used for work during the expansion process.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law