Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
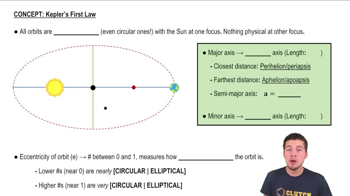
Elliptical Orbits
An elliptical orbit is a closed curve that describes the path of an object in space as it revolves around another object, such as a planet around the sun. The shape of the ellipse is defined by its semimajor axis and eccentricity, where the semimajor axis is the longest diameter of the ellipse, and eccentricity measures how much the orbit deviates from being circular.
Recommended video:
Speed and Energy of Elliptical Orbits
Semimajor Axis
The semimajor axis is half of the longest diameter of an ellipse and is a crucial parameter in determining the size of the orbit. For Pluto, the semimajor axis of 5.91 * 10^12 m indicates the average distance from the sun over one complete orbit, serving as a reference point for calculating its closest and farthest distances.
Recommended video:
Eccentricity
Eccentricity is a dimensionless parameter that quantifies the deviation of an orbit from a perfect circle. It ranges from 0 (circular orbit) to 1 (parabolic trajectory). For Pluto, an eccentricity of 0.249 indicates a moderately elongated orbit, which affects the variation in its distance from the sun throughout its orbit.
Recommended video: