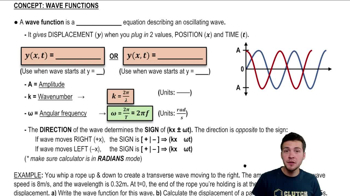
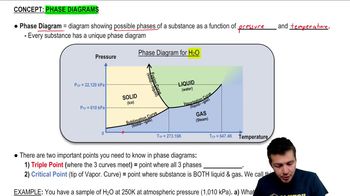
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Position Function
The position function describes the location of an object over time. In this case, the turtle's position is given by the equation x(t) = 50.0 cm + (2.00 cm/s)t − (0.0625 cm/s²)t², which includes a constant term, a linear term representing constant velocity, and a quadratic term indicating acceleration. Understanding this function is crucial for analyzing the turtle's motion.
Recommended video:
Velocity
Velocity is the rate of change of position with respect to time and is mathematically defined as the derivative of the position function. For the turtle, the velocity can be found by differentiating the position function x(t) with respect to time t. This will yield a new function v(t) that indicates how fast and in which direction the turtle is moving at any given time.
Recommended video:
Finding Critical Points
Critical points occur where the velocity of an object is zero, indicating a change in motion. To find when the turtle's velocity is zero, we set the velocity function v(t) equal to zero and solve for t. This process is essential for determining when the turtle stops moving forward or changes direction.
Recommended video: