Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Wave-Particle Duality
Wave-particle duality is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics that describes how particles, such as photons, exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This duality is crucial for understanding phenomena like interference and diffraction, as well as the quantization of energy in photons, which can be calculated using their wavelength.
Recommended video:
Intro to Waves and Wave Speed
Photon Energy and Frequency Relationship
The energy of a photon is directly related to its frequency through the equation E = hf, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is frequency. This relationship allows us to calculate the energy of a photon when its frequency is known, and vice versa, highlighting the intrinsic link between these two properties.
Recommended video:
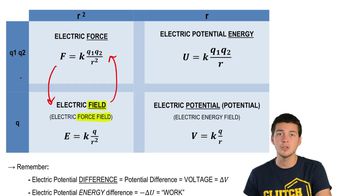
Relationships Between Force, Field, Energy, Potential
Momentum of a Photon
The momentum of a photon can be calculated using the formula p = E/c, where p is momentum, E is energy, and c is the speed of light. Despite having no mass, photons carry momentum due to their energy and the speed at which they travel, which is essential for understanding their interactions with matter, such as in the photoelectric effect.
Recommended video: