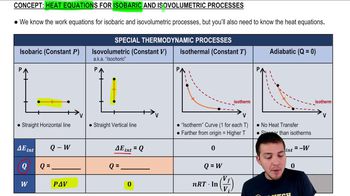
Textbook Question
5.0 g of nitrogen gas at 20°C and an initial pressure of 3.0 atm undergo an isobaric expansion until the volume has tripled.
a. What are the gas volume and temperature after the expansion?
281
views
 Knight Calc 5th Edition
Knight Calc 5th Edition Ch 19: Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics
Ch 19: Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Problem 19
Problem 19 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance