Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas through the equation PV = nRT. In this scenario, it is essential for calculating the final pressure of the argon gas after heating, as it allows us to understand how changes in temperature affect pressure when volume is constant.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gases and the Ideal Gas Law
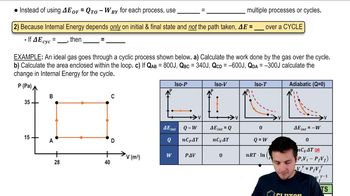
Isochoric Process
An isochoric process is one that occurs at constant volume. In this case, the argon gas is heated in a fixed volume container, meaning that any increase in temperature will directly affect the pressure of the gas, as described by the Ideal Gas Law. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing how the gas behaves under these conditions.
Recommended video:
Properties of Cyclic Thermodynamic Processes
Temperature Conversion
Temperature must be expressed in Kelvin when using the Ideal Gas Law. To convert Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature. In this problem, the initial and final temperatures of the gas must be converted to Kelvin to accurately calculate the final pressure after the isochoric heating.
Recommended video: