Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, calculated using the formula KE = 1/2 mv², where m is mass and v is velocity. In this scenario, the locomotive's kinetic energy at 10 m/s will determine how far it can roll before stopping, as this energy will be converted into work done against friction.
Recommended video:
Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy
Friction
Friction is the force that opposes the motion of an object when it is in contact with another surface. In this case, the friction between the locomotive's wheels and the track will act to decelerate the locomotive, ultimately bringing it to a stop. The coefficient of friction is crucial for calculating the distance traveled.
Recommended video:
Static Friction & Equilibrium
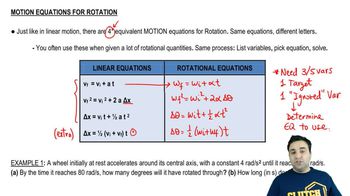
Equations of Motion
The equations of motion describe the relationship between an object's displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. For this problem, we can use the equation that relates initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration, and distance to find how far the locomotive rolls before stopping, given that the final velocity is zero.
Recommended video:
Equations of Rotational Motion