Fill in the following blanks.
a. 1 μm = ______ m
b. 1= _______ 10⁻⁹ m
c. 1 μm = ______ nm
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Fill in the following blanks.
a. 1 μm = ______ m
b. 1= _______ 10⁻⁹ m
c. 1 μm = ______ nm
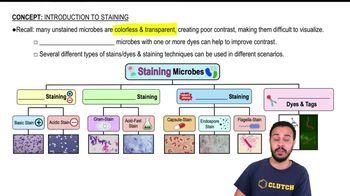
Assume you stain Bacillus by applying malachite green with heat and then counterstain with safranin. Through the microscope, the green structures are
a. cell walls.
b. capsules.
c. endospores.
d. flagella.
e. impossible to identify.
Which of the following is not a modification of a compound light microscope?
a. brightfield microscopy
b. darkfield microscopy
c. electron microscopy
d. phase-contrast microscopy
e. fluorescence microscopy
Three-dimensional images of live cells can be produced with
a. darkfield microscopy.
b. fluorescence microscopy.
c. transmission electron microscopy.
d. confocal microscopy.
e. phase-contrast microscopy.
Carbolfuchsin can be used as a simple stain and a negative stain. As a simple stain, the pH is
a. 2.
b. higher than the negative stain.
c. lower than the negative stain.
d. the same as the negative stain.
Calculate the total magnification of the nucleus of a cell being observed through a compound light microscope with a 10x ocular lens and an oil immersion lens.