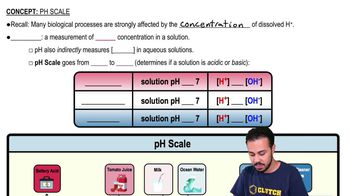
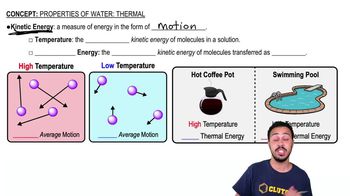
Which of the following is not a modification of a compound light microscope?
a. brightfield microscopy
b. darkfield microscopy
c. electron microscopy
d. phase-contrast microscopy
e. fluorescence microscopy
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Which of the following is not a modification of a compound light microscope?
a. brightfield microscopy
b. darkfield microscopy
c. electron microscopy
d. phase-contrast microscopy
e. fluorescence microscopy
Which type of microscope would be best to use to observe each of the following?
a. a stained bacterial smear
b. unstained bacterial cells: the cells are small, and no detail is needed
c. unstained live tissue when it is desirable to see some intracellular detail
d. a sample that emits light when illuminated with ultraviolet light
e. intracellular detail of a cell that is 1μm long
f. unstained live cells in which intracellular structures are shown in color
Three-dimensional images of live cells can be produced with
a. darkfield microscopy.
b. fluorescence microscopy.
c. transmission electron microscopy.
d. confocal microscopy.
e. phase-contrast microscopy.
Calculate the total magnification of the nucleus of a cell being observed through a compound light microscope with a 10x ocular lens and an oil immersion lens.
Looking at the cell of a photosynthetic microorganism, you observe the chloroplasts are green in brightfield microscopy and red in fluorescence microscopy. You conclude:
a. chlorophyll is fluorescent.
b. the magnification has distorted the image.
c. you’re not looking at the same structure in both microscopes.
d. the stain masked the green color.
e. none of the above
The maximum magnification of a compound microscope is (a) ________; that of an electron microscope, (b) ________. The maximum resolution of a compound microscope is (c) ________; that of an electron microscope, (d) ________. One advantage of a scanning electron microscope over a transmission electron microscope is (e) ________.