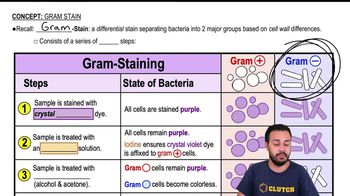
Gram Staining Procedure
The Gram staining procedure is a differential staining technique used to classify bacteria into two groups: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. It involves applying a series of dyes, including crystal violet, iodine, alcohol, and safranin, to bacterial cells. The outcome depends on the cell wall structure; Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain, appearing purple, while Gram-negative bacteria do not and take up the counterstain, appearing pink.
Recommended video:
Cell Wall Structure
The cell wall structure of bacteria is crucial for the Gram stain's effectiveness. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer that retains the crystal violet stain, while Gram-negative bacteria possess a thinner peptidoglycan layer surrounded by an outer membrane. This structural difference is key to understanding why the Gram stain differentiates these two groups and influences their susceptibility to antibiotics.
Recommended video:
Clinical Relevance of Gram Staining
Gram staining is clinically significant as it aids in the identification of bacterial pathogens and informs treatment decisions. The results can guide the choice of antibiotics, as Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria often respond differently to various drugs. Rapid identification through Gram staining can be critical in managing infections and improving patient outcomes.
Recommended video: