DRAW IT Draw a simple lipid, and show how it could be modified to a phospholipid.
Briefly describe the components of DNA, and explain its functional relationship to RNA and protein.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
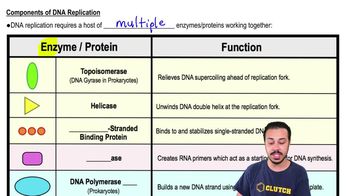
Components of DNA
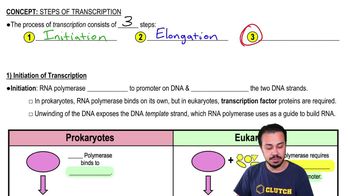
Transcription and RNA
Translation and Protein Synthesis

Macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) are often listed as CHONPS. What does each of these letters indicate, and why are they needed by the cell?
The term trace elements refers to
a. the elements CHONPS.
b. vitamins.
c. nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur.
d. small mineral requirements.
e. toxic substances.
Identify and mark each of the following on the portion of DNA undergoing replication: replication fork, DNA polymerase, RNA primer, parent strands, leading strand, lagging strand, the direction of replication on each strand, and the 5′ end of each strand. <IMAGE>
Match the following examples of mutagens. <IMAGE>
The following is a code for a strand of DNA.<IMAGE>
a. Using the genetic code provided in Figure 8.8, fill in the blanks to complete the segment of DNA shown.
b. Fill in the blanks to complete the sequence of amino acids coded for by this strand of DNA.
c. Write the code for the complementary strand of DNA completed in part (a).
d. What would be the effect if C were substituted for T at base 10?
e. What would be the effect if A were substituted for G at base 11?
f. What would be the effect if G were substituted for T at base 14?
g. What would be the effect if C were inserted between bases 9 and 10?
h. How would UV radiation affect this strand of DNA?
i. Identify a nonsense sequence in this strand of DNA.
