Define inflammation, and list its characteristics.
Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
All textbooks Tortora 14th Edition
Tortora 14th Edition Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Problem 16.3a
Problem 16.3a
 Tortora 14th Edition
Tortora 14th Edition Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
Ch. 16 - Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Problem 16.3a
Problem 16.3aChapter 12, Problem 16.3a
If the following are placed in the order of occurrence, which would be the third step?
a. diapedesis
b. digestion
c. formation of a phagosome
d. formation of a phagolysosome
e. margination
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the process of phagocytosis and the immune response.
Identify the sequence of events in phagocytosis: margination, diapedesis, phagosome formation, phagolysosome formation, and digestion.
Recognize that margination is the first step where white blood cells move to the blood vessel walls.
Acknowledge that diapedesis is the second step where white blood cells exit the blood vessels.
Determine that the formation of a phagosome is the third step, where the cell engulfs the pathogen.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Diapedesis
Diapedesis is the process by which white blood cells move out of the bloodstream and into tissues. This occurs during an immune response, allowing immune cells to reach sites of infection or injury. It is a crucial step in the inflammatory response, enabling the body to combat pathogens effectively.
Recommended video:
Guided course

3) Vasodilation
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is the process by which certain cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, engulf and digest pathogens or debris. This involves the formation of a phagosome, which is a vesicle that contains the ingested material. The phagosome then fuses with a lysosome to form a phagolysosome, where the material is broken down.
Recommended video:
Guided course
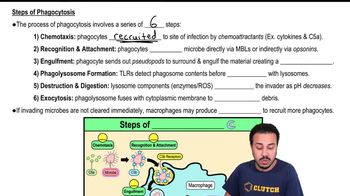
Steps of Phagocytosis
Phagolysosome Formation
The formation of a phagolysosome is a critical step in the immune response, occurring after a phagosome engulfs a pathogen. This vesicle then merges with a lysosome, which contains digestive enzymes, allowing for the breakdown of the engulfed material. This process is essential for the elimination of pathogens and the resolution of infection.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Formation & Breakdown of Polysaccharides
Related Practice
Textbook Question
109
views
Textbook Question
Chlamydia can prevent the formation of phagolysosomes and therefore can
a. avoid being phagocytized.
b. avoid destruction by complement.
c. prevent adherence.
d. avoid being digested.
e. none of the above
124
views
Textbook Question
What are interferons? Discuss their roles in innate immunity.
97
views
Textbook Question
How can the complement system cause endotoxic shock?
90
views
Textbook Question
If the following are placed in the order of occurrence, which would be the third step?
a. activation of C5 through C9
b. cell lysis
c. antigen–antibody reaction
d. activation of C3
e. activation of C2 through C4
106
views
Textbook Question
Patients with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease are susceptible to infections because their neutrophils don’t generate an oxidative burst. What is the relation of the oxidative burst to infection?
97
views