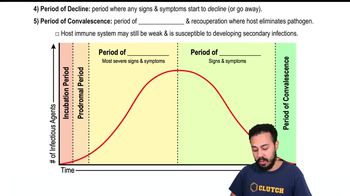
Use the following information to answer questions 6–7.
On September 6, a 6-year-old boy experienced fever, chills, and vomiting. On September 7, the child was hospitalized with diarrhea and swollen lymph nodes under both arms. On September 3, he had been scratched and bitten by a cat. The cat was found dead on September 5, and Y. pestis was isolated from the cat. Chloramphenicol was administered to the child from September 7, when Y. pestis was isolated from his blood. On September 17, the child's temperature returned to normal. On September 22, the child was released from the hospital.
Identify the incubation period for this case of bubonic plague.
a. September 3-5
b. September 3-6
c. September 6-7
d. September 6-17