Some antibiotics activate phage genes. MRSA releasing Panton-Valentine leukocidin is a toxin that can cause a life-threatening disease. Why can such a disease develop following antibiotic treatment?
Which of the following statements is false?
a. Viruses contain DNA or RNA.
b. The nucleic acid of a virus is surrounded by a protein coat.
c. Viruses multiply inside living cells using viral mRNA, tRNA, and ribosomes.
d. Viruses cause the synthesis of specialized infectious elements.
e. Viruses multiply inside living cells.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Structure of Viruses

Viral Replication

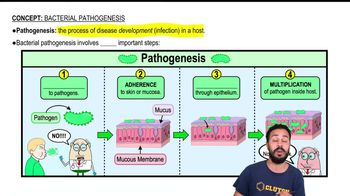
Viral Pathogenesis
The ability of a virus to infect an organism is regulated by
a. the host species.
b. the type of cells.
c. the availability of an attachment site.
d. cell factors necessary for viral replication.
e. all of the above
Recall from Chapter 1 that Koch's postulates are used to determine the etiology of a
disease. Why is it difficult to determine the etiology of
a. a viral infection, such as influenza?
b. cancer?
Persistent viral infections such as (a) ________ might be caused by (b) ________ that are (c) ________.
Place the following in the order in which they are found in a host cell: (1) capsid proteins;
(2) infective phage particles; (3) phage nucleic acid.
a. 1, 2, 3
b. 3, 2, 1
c. 2, 1,3
d. 3, 1, 2
e. 1, 3, 2
Plant viruses can’t penetrate intact plant cells because (a) ________; therefore, they enter cells by (b) ________. Plant viruses can be cultured in (c) ________.
