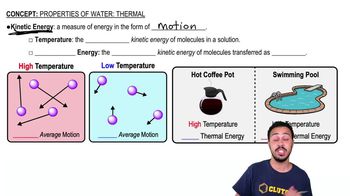
Which of the following types of media would not be used to culture aerobes?
a. selective media
b. reducing media
c. enrichment media
d. differential media
e. complex media
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Which of the following types of media would not be used to culture aerobes?
a. selective media
b. reducing media
c. enrichment media
d. differential media
e. complex media
The thermal death time for a suspension of Bacillus subtilis endospores is in dry heat and less than in an autoclave. Which type of heat is more effective? Why?
If pasteurization does not achieve sterilization, why is pasteurization used to treat food?
The antimicrobial effect of gamma radiation is due to (a) ________. The antimicrobial effect of ultraviolet radiation is due to (b) ________.
A mixed culture of Escherichia coli and Penicillium chrysogenum is inoculated onto the following culture media. On which medium would you expect each to grow? Why?
a. 0.5% peptone in tap water
b. 10% glucose in tap water
Differentiate cellular and plasmodial slime molds. How does each survive adverse environmental conditions?