Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Trophophase
The trophophase is the phase of microbial growth characterized by active cell division and biomass accumulation. During this phase, microorganisms utilize available nutrients to grow and reproduce, leading to the production of primary metabolites, such as amino acids and nucleotides, which are essential for cellular functions.
Idiophase
The idiophase follows the trophophase and is marked by a shift in metabolic activity as nutrients become limited. In this phase, microorganisms begin to produce secondary metabolites, which are not directly involved in growth but play crucial roles in survival, competition, and communication, such as antibiotics and pigments.
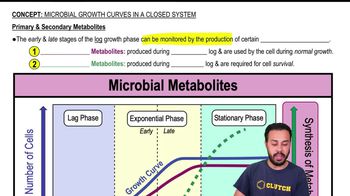
Primary and Secondary Metabolites
Primary metabolites are compounds produced during the growth phase that are essential for the normal growth and development of microorganisms, including proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. In contrast, secondary metabolites are produced during the idiophase and are often involved in ecological interactions, such as defense mechanisms or signaling, and are not necessary for basic cellular functions.
Recommended video:
Primary & Secondary Metabolites