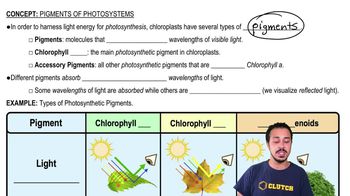
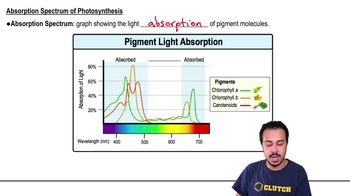
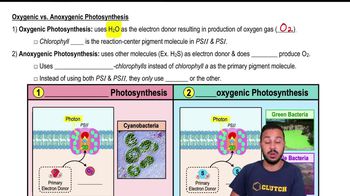
Match the descriptions below with their corresponding terms.
1. Occurs when energy from a compound containing phosphate reacts with ADP to form ATP
2. Involves formation of ATP via reduction of coenzymes in the electron transport chain
3. Begins with glycolysis
4. Occurs when all active sites on substrate molecules are filled
A. Saturation
B. Oxidative phosphorylation
C. Substrate-level phosphorylation
D. Photophosphorylation
E. Carbohydrate catabolism