Can nonliving things metabolize? Explain your answer.
Ch. 5 - Microbial Metabolism
Chapter 5, Problem 5.1a
Match the descriptions below with their corresponding terms.
1. Occurs when energy from a compound containing phosphate reacts with ADP to form ATP
2. Involves formation of ATP via reduction of coenzymes in the electron transport chain
3. Begins with glycolysis
4. Occurs when all active sites on substrate molecules are filled
A. Saturation
B. Oxidative phosphorylation
C. Substrate-level phosphorylation
D. Photophosphorylation
E. Carbohydrate catabolism
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the process described in statement 1: 'Occurs when energy from a compound containing phosphate reacts with ADP to form ATP'. This is known as Substrate-level phosphorylation.
Identify the process described in statement 2: 'Involves formation of ATP via reduction of coenzymes in the electron transport chain'. This is known as Oxidative phosphorylation.
Identify the process described in statement 3: 'Begins with glycolysis'. This is a part of Carbohydrate catabolism.
Identify the process described in statement 4: 'Occurs when all active sites on substrate molecules are filled'. This is known as Saturation.
Match each description with the corresponding term: 1 with C, 2 with B, 3 with E, and 4 with A.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a metabolic process where a phosphate group is directly transferred from a phosphorylated substrate to ADP, forming ATP. This occurs in specific reactions during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, allowing cells to generate ATP without the need for an electron transport chain.
Recommended video:
Guided course
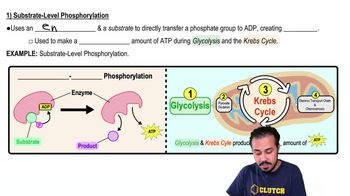
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a key metabolic pathway that produces ATP through the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. In this process, electrons from reduced coenzymes are transferred through a series of proteins, leading to the pumping of protons across a membrane, which drives ATP synthesis as protons flow back through ATP synthase.
Recommended video:
Guided course
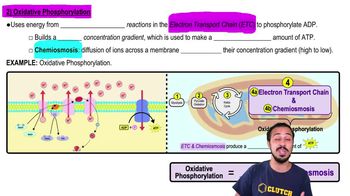
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Carbohydrate catabolism
Carbohydrate catabolism refers to the biochemical processes that break down carbohydrates to release energy. This includes glycolysis, where glucose is converted into pyruvate, followed by the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, ultimately leading to the production of ATP and other energy-rich molecules.
Recommended video:
Guided course
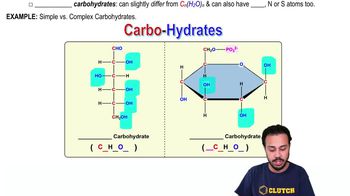
Carbohydrates
Related Practice
Textbook Question
64
views
Textbook Question
For each of the phrases in questions 1–7, indicate the type of metabolism referred to, using the following choices:
a. anabolism only
b. both anabolism and catabolism (amphibolic)
c. catabolism only
Breaks a large molecule into smaller ones
2
views
Textbook Question
Activation energy ______.
a. is the amount of energy required during an activity such as flagellar motion
b. requires the addition of nutrients in the presence of water
c. is lowered by the action of organic catalysts
d. results from the movement of molecules
79
views
Textbook Question
Label the mitochondrion to indicate the location of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport chains.
<IMAGE>
87
views
Textbook Question
How does amination differ from transamination?
77
views
Textbook Question
Why do cyanobacteria and algae take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen?
68
views
