Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
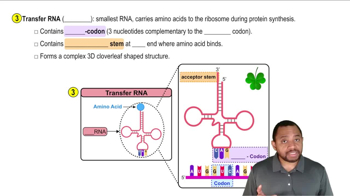
tRNA (Transfer RNA)
tRNA is a small RNA molecule, typically about 76 to 90 nucleotides long, that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis. It carries amino acids to the ribosome, where proteins are assembled according to the sequence of the mRNA. Due to its relatively short length, tRNA is the smallest among the three types of RNA mentioned.
Recommended video:
mRNA (Messenger RNA)
mRNA is a single-stranded RNA molecule that serves as a template for protein synthesis. It is synthesized from DNA during transcription and varies in length, typically ranging from hundreds to thousands of nucleotides, depending on the gene it encodes. mRNA is larger than tRNA but smaller than DNA, making it the intermediate in size between the two.
Recommended video:
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
DNA is the hereditary material in all living organisms and is composed of two long strands forming a double helix. It contains the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA molecules can be very large, often consisting of millions of nucleotides, making it the largest of the three types of nucleic acids.
Recommended video:
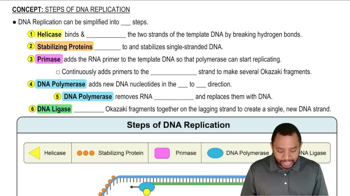
Steps of DNA Replication Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance