Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Definition of Electrolytes
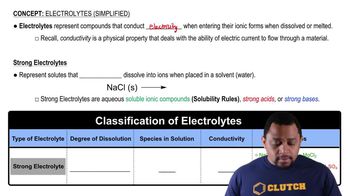
Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, allowing them to conduct electricity. Common examples include salts, acids, and bases. They play a crucial role in various biological processes, including nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
Recommended video:
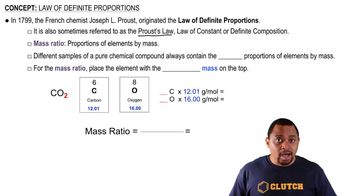
Law of Definite Proportions
Types of Electrolytes
Electrolytes can be categorized into strong and weak electrolytes. Strong electrolytes, like sodium chloride, completely dissociate into ions in solution, while weak electrolytes, such as acetic acid, only partially dissociate. This distinction affects their conductivity and reactivity in chemical processes.
Recommended video:
Electrolytes (Simplified) Concept 1
Importance of Electrolytes in Physiology
In the human body, electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium are vital for maintaining fluid balance, regulating blood pressure, and ensuring proper muscle and nerve function. Imbalances in electrolyte levels can lead to serious health issues, highlighting their importance in physiological processes.
Recommended video:
Electrolytes (Simplified) Concept 1