Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
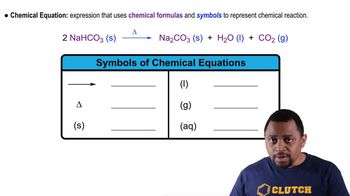
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula of a compound provides a concise representation of its molecular composition, indicating the number and types of atoms present. For ibuprofen, the formula is C13H18O2, which signifies it contains 13 carbon atoms, 18 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. Understanding chemical formulas is essential for identifying the structure and potential reactivity of compounds.
Recommended video:
Chemical Reaction: Chemical Change Concept 2
Pharmacological Uses
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. It is effective for various conditions, including headaches, muscle aches, arthritis, and menstrual cramps. Recognizing its pharmacological uses helps in understanding its role in pain management and its therapeutic applications.
Recommended video:
What is Chemistry? Concept 2
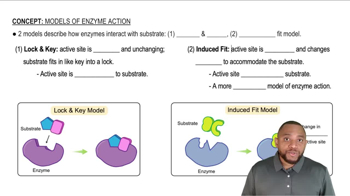
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of ibuprofen involves the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which play a crucial role in the synthesis of prostaglandins—compounds that mediate inflammation and pain. By blocking these enzymes, ibuprofen reduces the production of prostaglandins, leading to decreased inflammation and pain relief. This concept is vital for comprehending how ibuprofen functions at a biochemical level.
Recommended video:
Models of Enzyme Action Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance