Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
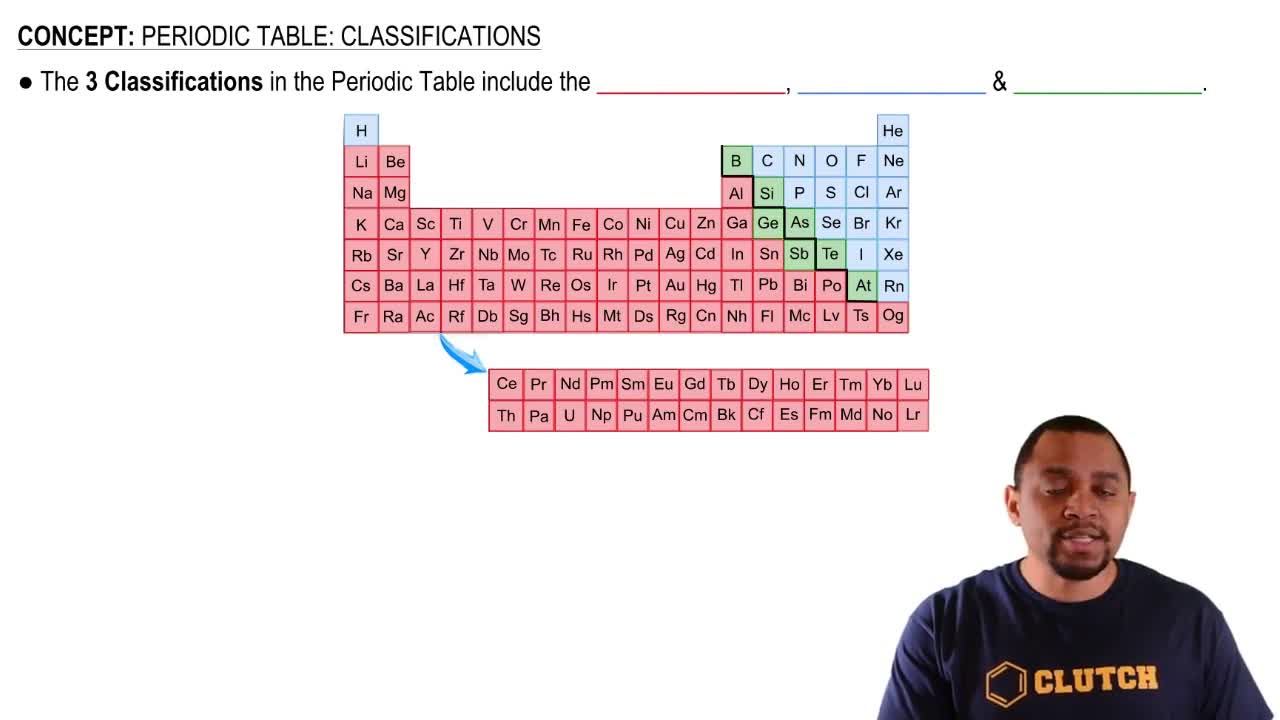
Periodic Table Structure
The periodic table is organized by increasing atomic number, with elements arranged in rows called periods. Each period corresponds to the filling of electron shells, which determines the chemical properties of the elements. The fourth period begins with potassium (atomic number 19) and ends with krypton (atomic number 36), encompassing 18 elements as it fills the 4s, 3d, and 4p subshells.
Recommended video:
Periodic Table: Classifications
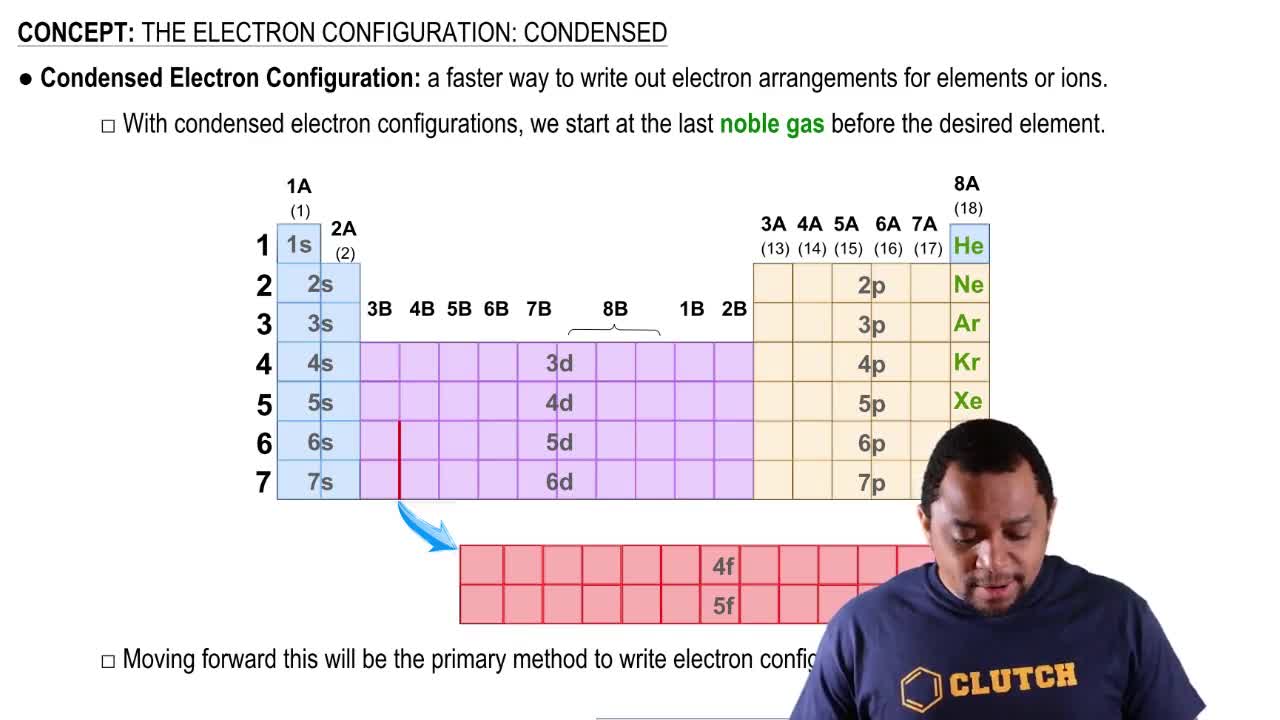
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals. For the fourth period, the filling of the 4s orbital occurs first, followed by the 3d and 4p orbitals. This configuration explains why there are 18 elements in this period, as it includes all the elements that can be formed with the available orbitals in that energy level.
Recommended video:
The Electron Configuration: Condensed
Subshells and Their Capacity
Subshells are divisions of electron shells that can hold a specific number of electrons. The 4s subshell can hold 2 electrons, the 3d subshell can hold 10 electrons, and the 4p subshell can hold 6 electrons. Therefore, the total capacity for the fourth period is 2 (4s) + 10 (3d) + 6 (4p) = 18 electrons, which corresponds to the 18 elements found in this period.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance