Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
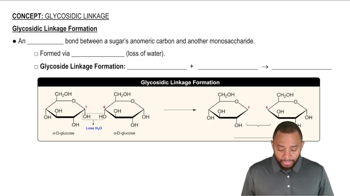
Glycosidic Bond
A glycosidic bond is a type of covalent bond that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which can be another carbohydrate or a different type of molecule. This bond forms through a dehydration reaction, where a water molecule is released. In disaccharides like mannobiose, the glycosidic bond is crucial for linking two monosaccharides, influencing the structure and properties of the resulting sugar.
Recommended video:
Glycosidic Linkage Formation Concept 1
Mannobiose Structure
Mannobiose is a disaccharide composed of two mannose units linked by a glycosidic bond. Understanding its structure is essential for identifying the specific type of glycosidic bond present. The configuration of the bond (alpha or beta) and the position of the linkage (1→2, 1→4, etc.) determine the properties and biological functions of mannobiose.
Recommended video:
Structural Formula Concept 2
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar units. They serve as the building blocks for more complex carbohydrates, such as disaccharides and polysaccharides. In the case of mannobiose, the two mannose monosaccharides are essential for understanding how they combine to form the disaccharide and the nature of the glycosidic bond that links them.
Recommended video:
Reduction of Monosaccharides Example 1