Textbook Question
Are the substances shown in italics undergoing oxidation or reduction?
(c) Wine (containing ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH) sours to vinegar (CH₃COOH).
8
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
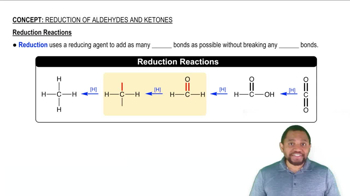

Are the substances shown in italics undergoing oxidation or reduction?
(c) Wine (containing ethanol, CH₃CH₂OH) sours to vinegar (CH₃COOH).
Are the substances shown in italics undergoing oxidation or reduction?
(c) The biomolecule FADH₂ loses hydrogen, becoming FAD.
ALLIED Health Identify the main organic reaction shown as condensation, hydrolysis, oxidation, or reduction:
(b) <IMAGE>
Write the products of the following reactions:
(b) <IMAGE>
Write the products of the following reactions:
(a) <IMAGE>
Fill in the missing organic products or reactants for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(a) <IMAGE>