Textbook Question
Identify the metabolic nucleotide described by the following:
a. contains the vitamin riboflavin
5
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
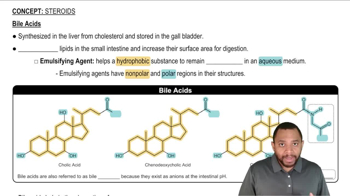
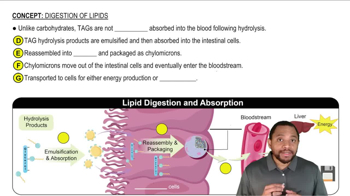
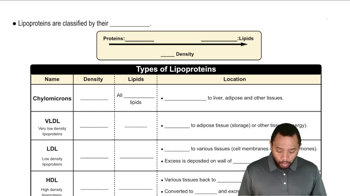
Identify the metabolic nucleotide described by the following:
a. contains the vitamin riboflavin
Identify the metabolic nucleotide described by the following:
a. contains a form of the vitamin niacin
Identify the metabolic nucleotide described by the following:
a. exchanges energy when a phosphate bond is hydrolyzed
Name the end products for digestion of proteins.
Name the starting reactant of glycolysis.
In terms of high-energy molecules, what is the net output for one molecule of glucose undergoing glycolysis?