Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phosphate Bond Hydrolysis
Phosphate bond hydrolysis refers to the chemical reaction where a phosphate group is removed from a nucleotide, releasing energy. This process is crucial in cellular metabolism, as it provides the energy needed for various biochemical reactions. The breaking of this bond typically occurs in nucleotides like ATP, which is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell.
Recommended video:
Acidic Hydrolysis Concept 1
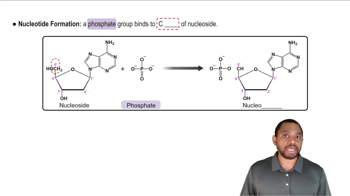
Nucleotide Structure
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids and consist of three components: a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. The presence of phosphate groups is essential for the nucleotide's role in energy transfer and storage. Understanding the structure of nucleotides helps in comprehending how they function in metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Nucleoside and Nucleotide Formation Concept 2
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a nucleotide that plays a central role in energy transfer within cells. It contains three phosphate groups, and when one of these phosphate bonds is hydrolyzed, it releases energy that can be used for cellular activities. ATP is vital for processes such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and biochemical synthesis.
Recommended video:
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Example 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance