Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Watson-Crick Model
The Watson-Crick model, proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, describes the double helix structure of DNA. It illustrates how two strands of DNA are held together by complementary base pairing between adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine. This model is fundamental for understanding how genetic information is stored and transmitted.
Recommended video:
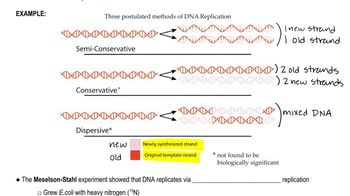
Semi-conservative Replication
The semi-conservative replication mechanism, as suggested by the Watson-Crick model, indicates that during DNA replication, each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This process ensures that genetic information is accurately passed on to daughter cells, maintaining the integrity of the genetic code across generations.
Recommended video:
Semiconservative Replication
Base Pairing
Base pairing refers to the specific hydrogen bonding between nucleotide bases in DNA, where adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. This complementary pairing is crucial for the accurate replication of DNA, as it ensures that each new strand is an exact copy of the original, facilitating the faithful transmission of genetic information.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance