Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
B-DNA and Z-DNA Structures
B-DNA is the most common form of DNA in cells, characterized by a right-handed helix with about 10.5 base pairs per turn. In contrast, Z-DNA is a left-handed helix that forms under certain conditions, such as high salt concentrations or specific sequences. Understanding these structural differences is crucial for analyzing the helical nature of DNA.
Recommended video:
Right-Handed vs. Left-Handed Helices
The terms 'right-handed' and 'left-handed' refer to the direction in which the helix twists. Right-handed helices, like B-DNA, twist clockwise when viewed from the top, while left-handed helices, like Z-DNA, twist counterclockwise. This distinction affects the physical properties and biological functions of the DNA.
Recommended video:
Helical Parameters
Helical parameters, such as pitch, rise per base pair, and base pair orientation, are essential for characterizing DNA structures. These parameters help determine the overall shape and stability of the helix. Analyzing these parameters allows for the identification of whether a given DNA structure is right-handed or left-handed.
Recommended video:
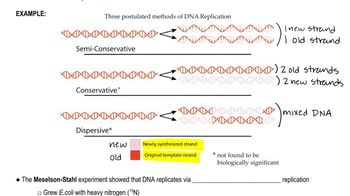
Semiconservative Replication