Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gene Duplication
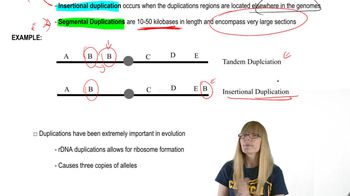
Gene duplication is a process where a segment of DNA is copied, resulting in two identical or similar genes. This can lead to the evolution of new functions as one gene may retain the original function while the other accumulates mutations over time. In the case of hemoglobin, the α and β globin genes likely arose from a common ancestral gene through duplication, allowing for specialization in function while maintaining some structural similarities.
Recommended video:
Chromosomal Location and Evolution
The location of genes on different chromosomes can influence their evolutionary paths. Genes that are located on separate chromosomes, like the α and β globin genes, can evolve independently, allowing for variations in expression and function. This separation can lead to the development of distinct polypeptides that still share functional roles, as seen in the cooperative binding of oxygen by hemoglobin.
Recommended video:
Functional Redundancy
Functional redundancy refers to the phenomenon where different genes or proteins can perform similar functions within a biological system. In the case of hemoglobin, the α and β chains exhibit functional redundancy in oxygen transport, allowing for a robust system that can adapt to varying physiological conditions. This redundancy can be advantageous, as it provides a backup mechanism if one polypeptide is mutated or not expressed.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance