Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Monosubstituted Benzene
Monosubstituted benzene refers to a benzene ring that has one substituent group attached to it. The presence of this substituent alters the chemical properties and reactivity of the benzene, allowing for various chemical reactions. Naming these compounds follows specific IUPAC rules, where the substituent is identified and the benzene ring is treated as the parent structure.
Recommended video:
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature provides a systematic method for naming chemical compounds. For monosubstituted benzenes, the substituent is named first, followed by 'benzene' as the base name. The position of the substituent is indicated by numbering the carbon atoms in the benzene ring, starting from the carbon attached to the substituent.
Recommended video:
Substituent Effects
Substituents on a benzene ring can influence the ring's reactivity and the orientation of further substitutions. They can be classified as electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups, affecting the electron density of the ring. Understanding these effects is crucial for predicting the outcomes of electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and for determining the stability of the resulting compounds.
Recommended video:
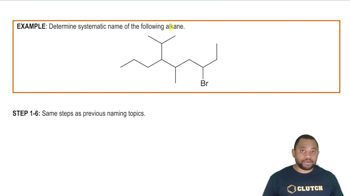
Naming Other Substituents Example