Consider the gas-phase reaction: H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g) The reaction was experimentally determined to be first order in H2 and first order in I2. Consider the proposed mechanisms. Proposed mechanism I: H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g) Single step Proposed mechanism II: I2(g) Δk1k-12 I(g) Fast H2( g) + 2 I( g) → k22 HI( g) Slow b. What kind of experimental evidence might lead you to favor mechanism II over mechanism I?
The half-life for radioactive decay (a first-order process) of plutonium- 239 is 24,000 years. How many years does it take for one mole of this radioactive material to decay until just one atom remains?

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Half-Life

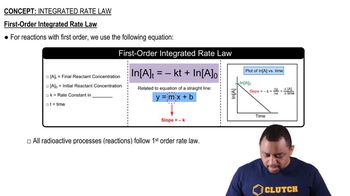
First-Order Kinetics
Exponential Decay

Phosgene (Cl2CO), a poison gas used in World War I, is formed
by the reaction of Cl2 and CO. The proposed mechanism for the
reaction is:
Cl2Δ2 Cl (fast, equilibrium)
Cl + COΔClCO (fast, equilibrium)
ClCO + Cl2¡Cl2CO + Cl (slow)
A certain substance X decomposes. Fifty percent of X remains after 100 minutes. How much X remains after 200 minutes if the reaction order with respect to X is (c) second order?
Ethyl chloride vapor decomposes by the first-order reaction: C2H5Cl → C2H4 + HCl The activation energy is 249 kJ/mol, and the frequency factor is 1.6⨉1014 s-1. Find the value of the rate constant at 710 K.
Ethyl chloride vapor decomposes by the first-order reaction: C2H5Cl → C2H4 + HCl The activation energy is 249 kJ/mol, and the frequency factor is 1.6⨉1014 s-1. What fraction of the ethyl chloride decomposes in 15 minutes at this temperature?
When HNO2 is dissolved in water, it partially dissociates according to the equation HNO2 ⇌ H+ + NO2-. A solution is prepared that contains 7.050 g of HNO2 in 1.000 kg of water. Its freezing point is -0.2929 °C. Calculate the fraction of HNO2 that has dissociated.
