Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. a. N2
Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory
All textbooks Tro 6th Edition
Tro 6th Edition Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory
Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory Problem 44
Problem 44
 Tro 6th Edition
Tro 6th Edition Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory
Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory Problem 44
Problem 44Chapter 11, Problem 44
Each ball-and-stick model shows the electron and molecular geometry of a generic molecule. Explain what is wrong with each molecular geometry and provide the correct molecular geometry, given the number of lone pairs and bonding groups on the central atom. (c)


Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs around a central atom. According to this theory, electron pairs, whether bonding or lone pairs, will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, leading to specific molecular shapes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
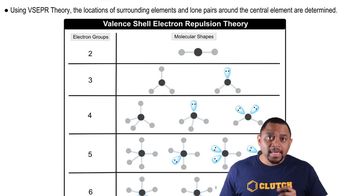
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR
Lone Pairs vs. Bonding Pairs
In molecular geometry, lone pairs are non-bonding pairs of electrons that occupy space around the central atom, influencing its shape. Bonding pairs, on the other hand, are shared between atoms to form bonds. The presence of lone pairs can distort the ideal bond angles and alter the expected geometry of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Electron Groups, Lone Pairs, and Bonding Groups Example
Molecular Geometry vs. Electron Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule, while electron geometry considers the spatial arrangement of all electron pairs, including lone pairs. Understanding the distinction is crucial, as the presence of lone pairs can lead to different molecular geometries than what would be predicted based solely on bonding pairs.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Electron Geometry
Related Practice
Textbook Question
485
views
Textbook Question
Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. b. N2H2 (skeletal structure HNNH)
751
views
Textbook Question
Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. c. N2H4 (skeletal structure H2NNH2)
874
views
Textbook Question
Determine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.) a. CH3OH (H3COH) b. CH3OCH3 (H3COCH3)
427
views
Textbook Question
Determine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.) c. H2O2 (HOOH)
968
views
Textbook Question
Determine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.)
a. CH3NH2 (H3CNH2)
b. CH3CO2CH3 (H3CCOOCH3 One O atom attached to 2nd C atom; the other O atom is bonded to the 2nd and 3rd C atom)
1814
views