Determine the molecular geometry and sketch each molecule or ion, using the bond conventions shown in “Representing Molecular Geometries on Paper” in Section 11.4. d. IF2–
 Tro 6th Edition
Tro 6th Edition Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory
Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory Problem 42b
Problem 42bDetermine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. b. N2H2 (skeletal structure HNNH)

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
VSEPR Theory
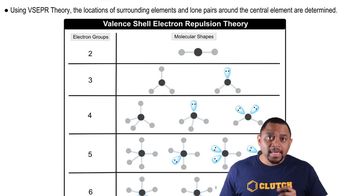
Molecular Geometry

Lewis Structures

Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and draw each molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.)
a. C2H2 (skeletal structure HCCH)
b. C2H4 (skeletal structure H2CCH2)
c. C2H6 (skeletal structure H3CCH3)
Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. a. N2
Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. c. N2H4 (skeletal structure H2NNH2)
Each ball-and-stick model shows the electron and molecular geometry of a generic molecule. Explain what is wrong with each molecular geometry and provide the correct molecular geometry, given the number of lone pairs and bonding groups on the central atom. (c)
Determine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.) a. CH3OH (H3COH) b. CH3OCH3 (H3COCH3)