Determine the molecular geometry about each interior atom and sketch each molecule. c. N2H4 (skeletal structure H2NNH2)
 Tro 6th Edition
Tro 6th Edition Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory
Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory Problem 45c
Problem 45cDetermine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.) c. H2O2 (HOOH)

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
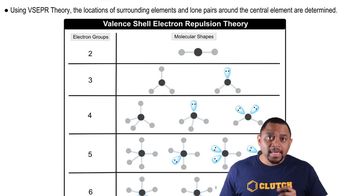
Molecular Geometry

VSEPR Theory
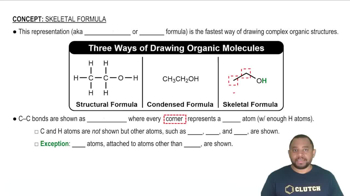
Skeletal Structure
Each ball-and-stick model shows the electron and molecular geometry of a generic molecule. Explain what is wrong with each molecular geometry and provide the correct molecular geometry, given the number of lone pairs and bonding groups on the central atom. (c)
Determine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.) a. CH3OH (H3COH) b. CH3OCH3 (H3COCH3)
Determine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.)
a. CH3NH2 (H3CNH2)
b. CH3CO2CH3 (H3CCOOCH3 One O atom attached to 2nd C atom; the other O atom is bonded to the 2nd and 3rd C atom)
Determine the geometry about each interior atom in each molecule and sketch the molecule. (Skeletal structure is indicated in parentheses.) c. NH2CO2H (H2NCOOH both O atoms attached to C)
Explain why CO2 and CCl4 are both nonpolar even though they contain polar bonds.