Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkene Structure
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). This unsaturation makes them more reactive than alkanes, allowing them to undergo various addition reactions. The geometry around the double bond is typically trigonal planar, which influences the orientation of the addition products.
Recommended video:
Addition Reactions
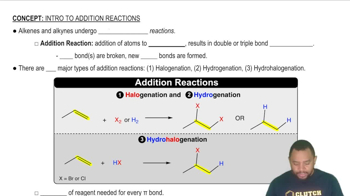
Addition reactions involve the addition of atoms or groups across the double bond of an alkene, converting it into a saturated compound. Common types of addition reactions include hydrogenation (adding H2), halogenation (adding X2), and hydrohalogenation (adding HX). The specific conditions and reagents used determine the nature of the products formed.
Recommended video:
Markovnikov's Rule
Markovnikov's Rule states that in the addition of HX to an alkene, the hydrogen atom will attach to the carbon with the greater number of hydrogen atoms already attached. This rule helps predict the major product of reactions involving unsymmetrical alkenes, leading to the formation of more stable carbocation intermediates during the reaction process.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance