Given the values of ΔH°rxn, ΔS°rxn, and T, determine ΔSuniv and predict whether or not each reaction is spontaneous. (Assume that all reactants and products are in their standard states.) c. ΔH°rxn = +95 kJ; ΔS°rxn = -157 J/K; T = 298 K
Predict the conditions (high temperature, low temperature, all temperatures, or no temperatures) under which each reaction is spontaneous. a. H2O(g) → H2O(l) b. CO2(s) → CO2(g) c. H2(g) → 2 H(g) d. 2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g) (endothermic)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Gibbs Free Energy

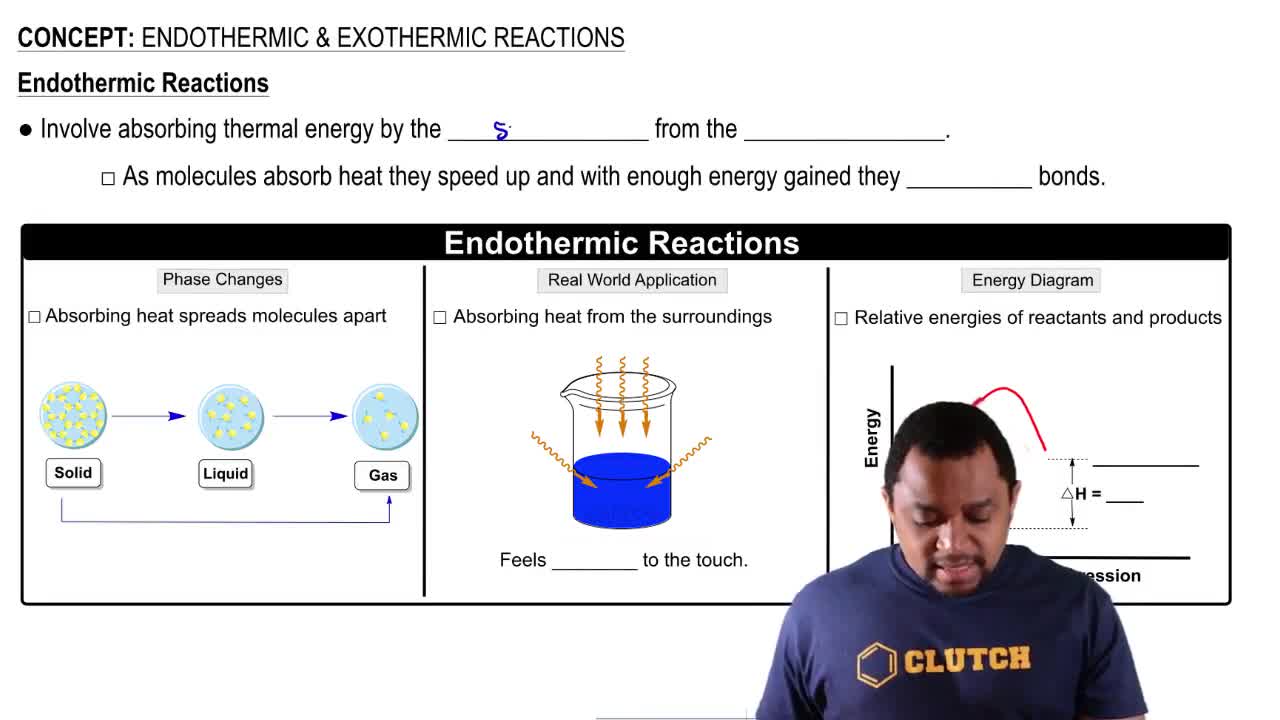
Endothermic Reactions
Entropy and Temperature

Calculate the free energy change for this reaction at 25 °C. Is the reaction spontaneous? (Assume that all reactants and products are in their standard states.) 2 Ca(s) + O2( g) → 2 CaO(s) ΔH°rxn = -1269.8 kJ; ΔS°rxn = -364.6 J/K
Fill in the blanks in the table. Both ΔH and ΔS refer to the system.
How does the molar entropy of a substance change with increasing temperature?
For each pair of substances, choose the one that you expect to have the higher standard molar entropy (S°) at 25 °C. Explain your choices. a. CO(g); CO2(g) b. CH3OH(l); CH3OH(g) c. Ar(g); CO2(g) d. CH4(g); SiH4(g) e. NO2(g); CH3CH2CH3(g) f. NaBr(s); NaBr(aq)
Rank each set of substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy (S°). Explain your reasoning. a. NH3(g); Ne(g); SO2(g); CH3CH2OH(g); He(g) c. CH4(g); CF4(g); CCl4(g)
