Fill in the blanks in the table. Both ΔH and ΔS refer to the system.
For each pair of substances, choose the one that you expect to have the higher standard molar entropy (S°) at 25 °C. Explain your choices. a. CO(g); CO2(g) b. CH3OH(l); CH3OH(g) c. Ar(g); CO2(g) d. CH4(g); SiH4(g) e. NO2(g); CH3CH2CH3(g) f. NaBr(s); NaBr(aq)

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Standard Molar Entropy (S°)

Molecular Complexity
Gas Phase Behavior
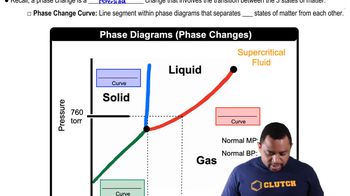
Predict the conditions (high temperature, low temperature, all temperatures, or no temperatures) under which each reaction is spontaneous. a. H2O(g) → H2O(l) b. CO2(s) → CO2(g) c. H2(g) → 2 H(g) d. 2 NO2(g) → 2 NO(g) + O2(g) (endothermic)
How does the molar entropy of a substance change with increasing temperature?
Rank each set of substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy (S°). Explain your reasoning. a. NH3(g); Ne(g); SO2(g); CH3CH2OH(g); He(g) c. CH4(g); CF4(g); CCl4(g)
Rank each set of substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy (S°). Explain your reasoning. b. H2O(s); H2O(l); H2O(g)
Rank each set of substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy (S°). Explain your reasoning. a. I2(g); F2(g); Br2(g); Cl2(g) b. H2O(g); H2O2(g); H2S(g) c. C(s, graphite); C(s, diamond); C(s, amorphous)
