Calculate the freezing point and boiling point of each aqueous solution, assuming complete dissociation of the solute. c. 5.5% NaNO3 by mass (in water)
A 1.2 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound with the formula MX2 has a boiling point of 101.4 °C. Calculate the van't Hoff factor (i) for MX2 at this concentration.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceRecommended similar problem, with video answer:

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
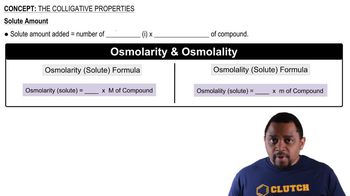
Colligative Properties
Boiling Point Elevation

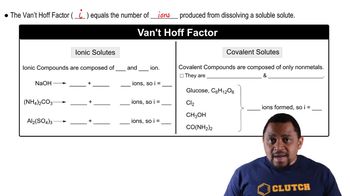
van't Hoff Factor (i)
What mass of salt (NaCl) should you add to 1.00 L of water in an ice cream maker to make a solution that freezes at -10.0 °C? Assume complete dissociation of the NaCl and density of 1.00 g/mL for water.
Use the van't Hoff factors in Table 13.9 to calculate each colligative property: a. the melting point of a 0.100 m iron(III) chloride solution
A 0.100 M ionic solution has an osmotic pressure of 8.3 atm at 25 °C. Calculate the van't Hoff factor (i) for this solution.
Calculate the vapor pressure at 25 °C of an aqueous solution that is 5.50% NaCl by mass. (Assume complete dissociation of the solute.)
An aqueous CaCl2 solution has a vapor pressure of 81.6 mmHg at 50 °C. The vapor pressure of pure water at this temperature is 92.6 mmHg. What is the concentration of CaCl2 in mass percent? (Assume complete dissociation of the solute.)
