What mass of salt (NaCl) should you add to 1.00 L of water in an ice cream maker to make a solution that freezes at -10.0 °C? Assume complete dissociation of the NaCl and density of 1.00 g/mL for water.
A 0.100 M ionic solution has an osmotic pressure of 8.3 atm at 25 °C. Calculate the van't Hoff factor (i) for this solution.

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
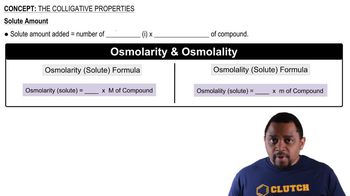
Osmotic Pressure

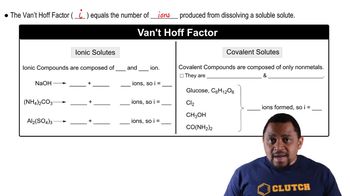
van't Hoff Factor (i)
Colligative Properties
Use the van't Hoff factors in Table 13.9 to calculate each colligative property: a. the melting point of a 0.100 m iron(III) chloride solution
A 1.2 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound with the formula MX2 has a boiling point of 101.4 °C. Calculate the van't Hoff factor (i) for MX2 at this concentration.
Calculate the vapor pressure at 25 °C of an aqueous solution that is 5.50% NaCl by mass. (Assume complete dissociation of the solute.)
An aqueous CaCl2 solution has a vapor pressure of 81.6 mmHg at 50 °C. The vapor pressure of pure water at this temperature is 92.6 mmHg. What is the concentration of CaCl2 in mass percent? (Assume complete dissociation of the solute.)
The solubility of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in water at 25 °C is 1.2 g/L. The solubility of chloroform (CHCl3) at the same temperature is 10.1 g/L. Why is chloroform almost ten times more soluble in water than carbon tetrachloride?
